How to Talk to Loved Ones About Their Hearing Loss
Talking to a loved one about hearing loss can be a sensitive topic,

Talking to a loved one about hearing loss can be a sensitive topic,
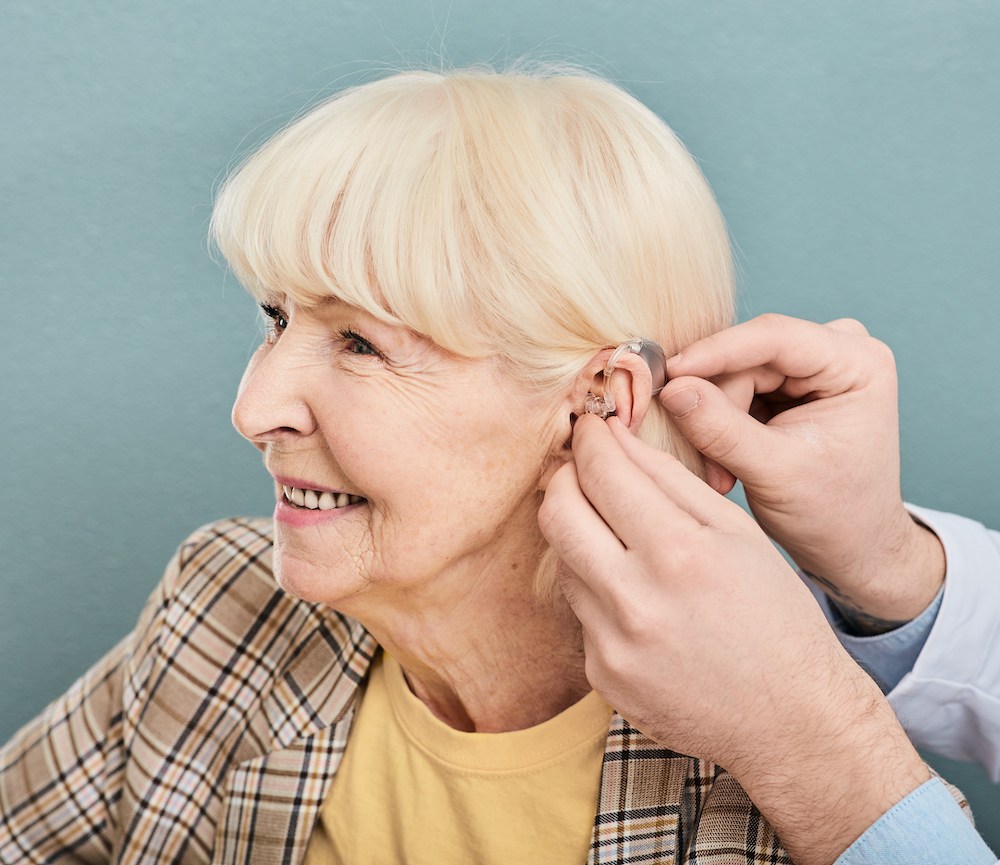
Binaural hearing aid processing is a listening approach where both hearing
During pregnancy, your body goes through many changes, some of which may