How to Support Veterans with Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is a challenge that many veterans face, often emerging long
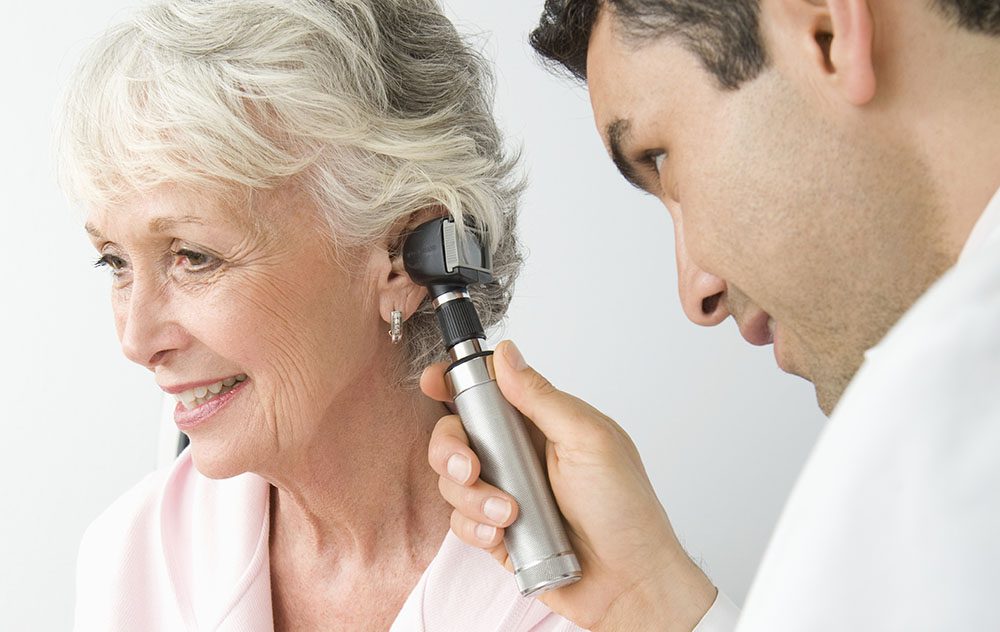

Hearing loss is a challenge that many veterans face, often emerging long

Finding out that your child may have hearing loss often brings up

Wondering how hearing loss might be affecting your performance at work?